Why 16 MHz is a Common Choice in Oscillators
In the world of electronic components, terms like 16 MHz are commonly used, but what do they really mean, and how should engineers and procurement professionals interpret these values? Let’s break down the essentials to help you understand frequency ratings in oscillators and connectors.
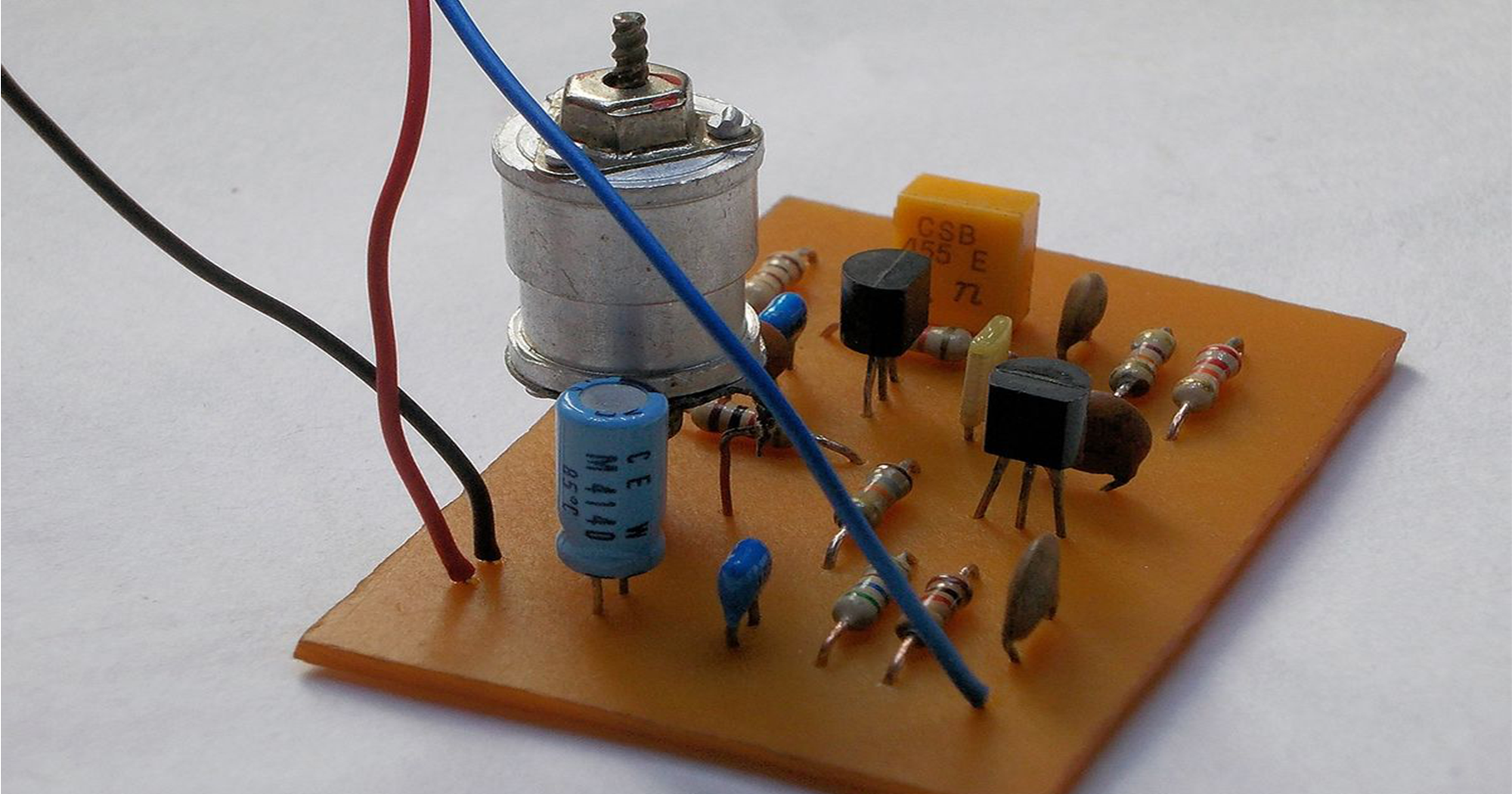
What Does "16 MHz" Mean in Oscillators?
The "16 MHz" in 16 MHz XO (Crystal Oscillator) refers to the frequency at which the oscillator operates—16 million cycles per second. Frequency is a measure of how many oscillations (or cycles) occur in one second. For this component, the oscillator generates a stable clock signal at 16 MHz, which is crucial for timing applications in electronic circuits.
MHz (Megahertz): The unit of frequency used here. 1 MHz equals 1 million cycles per second.
Why 16 MHz?: The specific frequency of 16 MHz is commonly used in various electronic devices like microcontrollers, communication equipment, and even older legacy systems. The frequency determines the speed at which the oscillator works and interacts with other components in the circuit.
How to Judge Whether the Frequency is High or Low
When selecting components like oscillators, the frequency value plays a key role in determining how fast or slow the device operates. Here’s how to judge the frequency:
Low Frequency: Frequencies below 10 MHz, like 1 MHz or 5 MHz, are typically used for low-speed applications such as basic microcontrollers or simple communication systems.
Standard Frequency: 16 MHz, 32 MHz, and similar values are considered standard for many common devices, offering a balanced performance for typical consumer electronics and embedded systems.
High Frequency: Frequencies above 100 MHz (like 200 MHz, 500 MHz) are used for high-speed applications, including high-performance microprocessors, telecommunications, and advanced computing systems.
The higher the frequency, the faster the circuit will operate, but it also requires more power and may generate more heat. Conversely, lower frequencies are energy-efficient but may not provide the same processing power.
How to Choose the Right Frequency for Your Application
Selecting the correct frequency for your project or product depends on several factors:
Application Requirements: What does the circuit need to do? For a basic microcontroller, a frequency of 16 MHz may be sufficient. For high-speed data processing, you might need something higher.
Power Consumption: Higher frequencies often require more power, so choose a lower frequency if your design prioritizes low power consumption.
Timing Accuracy: The accuracy of the clock signal can affect the performance of your device. Ensure that the oscillator you choose meets the timing requirements of your system.
When evaluating oscillators or other frequency-dependent components, always refer to the datasheet to check other important parameters like stability, accuracy, and tolerance.
Conclusion
The frequency value, such as 16 MHz, in oscillators is crucial for determining the performance and suitability of a component in your electronic system. For engineers and procurement professionals, understanding the relationship between frequency and component behavior helps in selecting the right parts for the right applications. Whether you're designing a basic device or a high-performance system, understanding these frequency guidelines will ensure your project is on the right track.
Some Model Numbers